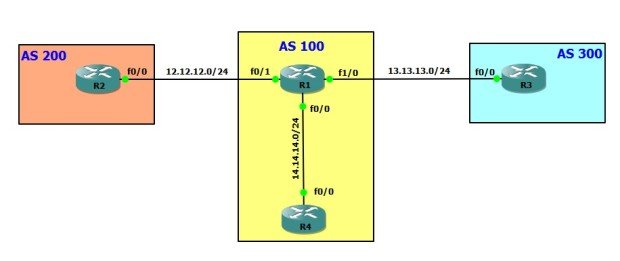
We will discuss the different ways to advertise a default route in BGP. We will use following network topology for the same.
1. default-information originate
A default route can be injected into BGP with the command ‘default-information originate’. Following conditions must be fulfilled to use this method.
– A default route must be in the local routing table.
– The default route must be redistributed into the BGP
– Add ‘default-information originate’ under router bgp <ASN>
Here is the initial configuration and BGP status on all routers.
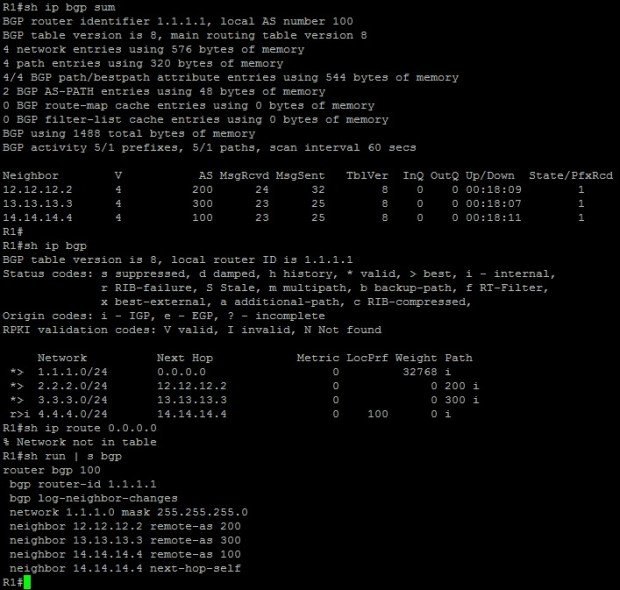
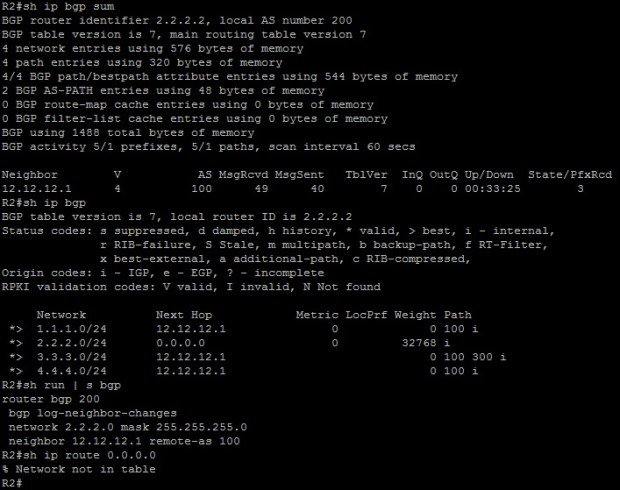
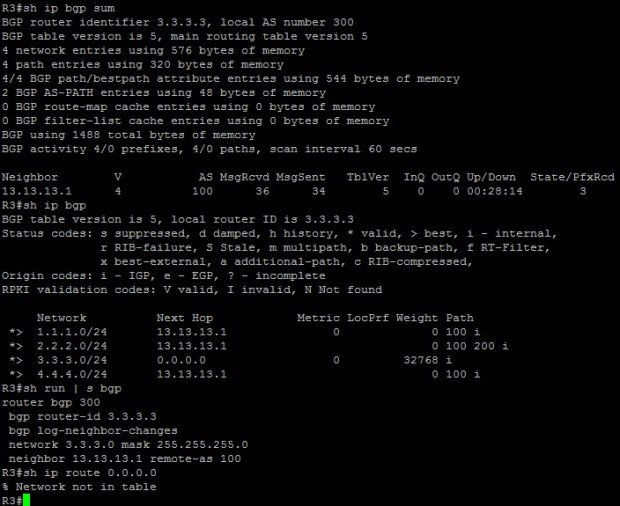
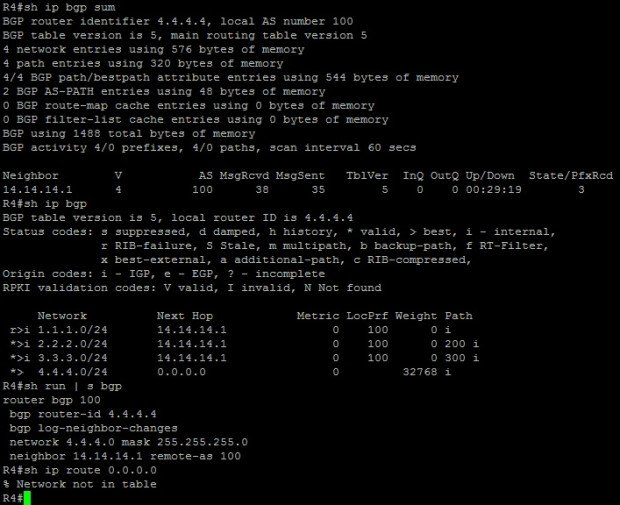
Let’s first try to add a static default route and redistribute it into BGP on R1.
R1#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 null0
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#redistribute static
R1(config-router)#
R1(config-router)#do sh run | s bgp
router bgp 100
bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
redistribute static
neighbor 12.12.12.2 remote-as 200
neighbor 13.13.13.3 remote-as 300
neighbor 14.14.14.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 14.14.14.4 next-hop-self
R1(config-router)#do sh ip route 0.0.0.0
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "static", distance 1, metric 0 (connected), candidate default path
Redistributing via bgp 100
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* directly connected, via Null0
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
R1(config-router)#
R1(config-router)#do sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 12.12.12.2 0 0 200 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 13.13.13.3 0 0 300 i
r>i 4.4.4.0/24 14.14.14.4 0 100 0 i
R1(config-router)#
R1 is not yet advertising default route into BGP. It shows that simply redistributing a default route into BGP would not help. Let’s add a ‘default-information originate’ under BGP.
R1(config-router)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#default-information originate
R1(config-router)#do sh run | s bgp
router bgp 100
bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
redistribute static
neighbor 12.12.12.2 remote-as 200
neighbor 13.13.13.3 remote-as 300
neighbor 14.14.14.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 14.14.14.4 next-hop-self
default-information originate
R1(config-router)#do sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 11, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 ?
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 12.12.12.2 0 0 200 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 13.13.13.3 0 0 300 i
r>i 4.4.4.0/24 14.14.14.4 0 100 0 i
R1(config-router)#
Now you can see all BGP peers (iBGP and eBGP) are receiving default route information from R1.
R2#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 2.2.2.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 0.0.0.0 12.12.12.1 0 0 100 ?
*> 1.1.1.0/24 12.12.12.1 0 0 100 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 12.12.12.1 0 100 300 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 12.12.12.1 0 100 i
R2#sh ip route 0.0.0.0
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "bgp 200", distance 20, metric 0, candidate default path
Tag 100, type external
Last update from 12.12.12.1 00:02:25 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 12.12.12.1, from 12.12.12.1, 00:02:25 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 1
Route tag 100
MPLS label: none
R2#
R3#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 8, local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 0.0.0.0 13.13.13.1 0 0 100 ?
*> 1.1.1.0/24 13.13.13.1 0 0 100 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 13.13.13.1 0 100 200 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 13.13.13.1 0 100 i
R3#sh ip route 0.0.0.0
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "bgp 300", distance 20, metric 0, candidate default path
Tag 100, type external
Last update from 13.13.13.1 00:04:36 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 13.13.13.1, from 13.13.13.1, 00:04:36 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 1
Route tag 100
MPLS label: none
R3#
R4#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 8, local router ID is 4.4.4.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i 0.0.0.0 14.14.14.1 0 100 0 ?
r>i 1.1.1.0/24 14.14.14.1 0 100 0 i
*>i 2.2.2.0/24 14.14.14.1 0 100 0 200 i
*>i 3.3.3.0/24 14.14.14.1 0 100 0 300 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
R4#sh ip route 0.0.0.0
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "bgp 100", distance 200, metric 0, candidate default path, type internal
Last update from 14.14.14.1 00:05:21 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 14.14.14.1, from 14.14.14.1, 00:05:21 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 0
MPLS label: none
2. network 0.0.0.0
A default route can be injected into BGP with configuration of ‘network 0.0.0.0’ under BGP if a default route is available in the local routing table of a router.
Following conditions must be fulfilled to use this method.
– A default route must be in the local routing table.
– Add ‘network 0.0.0.0’ under router bgp <ASN>
Let’s remove previously configured ‘default-information originate’ and ‘redistribute static’ commands and use ‘network 0.0.0.0’.
R1#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#no default-information originate
R1(config-router)#no redistribute static
R1(config-router)#network 0.0.0.0
R1(config-router)#do sh run | s bgp
router bgp 100
bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 0.0.0.0
network 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 12.12.12.2 remote-as 200
neighbor 13.13.13.3 remote-as 300
neighbor 14.14.14.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 14.14.14.4 next-hop-self
R1(config-router)#end
R1#sh ip
*Mar 24 11:42:36.623: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
R1#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 13, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 12.12.12.2 0 0 200 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 13.13.13.3 0 0 300 i
r>i 4.4.4.0/24 14.14.14.4 0 100 0 i
R1#
Let’s verify BGP table and default route on peer routers.
R2#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 12, local router ID is 2.2.2.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 0.0.0.0 12.12.12.1 0 0 100 i
*> 1.1.1.0/24 12.12.12.1 0 0 100 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 12.12.12.1 0 100 300 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 12.12.12.1 0 100 i
R2#sh ip route 0.0.0.0
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "bgp 200", distance 20, metric 0, candidate default path
Tag 100, type external
Last update from 12.12.12.1 00:01:54 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 12.12.12.1, from 12.12.12.1, 00:01:54 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 1
Route tag 100
MPLS label: none
R3#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 0.0.0.0 13.13.13.1 0 0 100 i
*> 1.1.1.0/24 13.13.13.1 0 0 100 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 13.13.13.1 0 100 200 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 13.13.13.1 0 100 i
R3#sh ip route 0.0.0.0
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "bgp 300", distance 20, metric 0, candidate default path
Tag 100, type external
Last update from 13.13.13.1 00:02:17 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 13.13.13.1, from 13.13.13.1, 00:02:17 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 1
Route tag 100
MPLS label: none
R4#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 4.4.4.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i 0.0.0.0 14.14.14.1 0 100 0 i
r>i 1.1.1.0/24 14.14.14.1 0 100 0 i
*>i 2.2.2.0/24 14.14.14.1 0 100 0 200 i
*>i 3.3.3.0/24 14.14.14.1 0 100 0 300 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
R4#sh ip route 0.0.0.0
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "bgp 100", distance 200, metric 0, candidate default path, type internal
Last update from 14.14.14.1 00:03:06 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 14.14.14.1, from 14.14.14.1, 00:03:06 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 0
MPLS label: none
3. neighbor x.x.x.x default-originate
If you want to advertise default route to a specific peer, this is the method for that requirement.
– Add ‘neighbor x.x.x.x default-originate’ under router bgp <ASN>
– It does not even check for the existence of a default route in the IP routing table
– The ‘default-information originate’ command should not be configured with the ‘neighbor x.x.x.x default-originate’ command on the same router
Let’s remove previously configured commands.
R1#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R1(config)#no ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Null0
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#no network 0.0.0.0
R1(config-router)#end
R1#sh run
*Mar 24 11:50:22.479: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
R1#sh run | s bgp
router bgp 100
bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 12.12.12.2 remote-as 200
neighbor 13.13.13.3 remote-as 300
neighbor 14.14.14.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 14.14.14.4 next-hop-self
R1#sh ip route 0.0.0.0
% Network not in table
R1#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 14, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 12.12.12.2 0 0 200 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 13.13.13.3 0 0 300 i
r>i 4.4.4.0/24 14.14.14.4 0 100 0 i
Now advertise default route only to R2.
R1#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#neighbor 12.12.12.2 default-originate
R1(config-router)#end
R1#s
*Mar 24 11:53:46.471: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by consoleh
R1#sh run | s bgp
router bgp 100
bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 12.12.12.2 remote-as 200
neighbor 12.12.12.2 default-originate
neighbor 13.13.13.3 remote-as 300
neighbor 14.14.14.4 remote-as 100
neighbor 14.14.14.4 next-hop-self
R1#clear ip bgp 12.12.12.2 soft
R1#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 15, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 0 i
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 12.12.12.2 0 0 200 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 13.13.13.3 0 0 300 i
r>i 4.4.4.0/24 14.14.14.4 0 100 0 i
R1#sh ip route 0.0.0.0
% Network not in table
R1#
Notice there is no default route available in local routing table of R1 and bgp table also shows there is no best route (no *> status) for 0.0.0.0 network.
Let’s verify what R1 is advertising to its peers.
R1#sh ip bgp neighbors 12.12.12.2 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 15, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Originating default network 0.0.0.0
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 13.13.13.3 0 0 300 i
r>i 4.4.4.0/24 14.14.14.4 0 100 0 i
Total number of prefixes 3
R1#sh ip bgp neighbors 13.13.13.3 advertised-routes
BGP table version is 15, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 12.12.12.2 0 0 200 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 13.13.13.3 0 0 300 i
r>i 4.4.4.0/24 14.14.14.4 0 100 0 i
Total number of prefixes 4
## No default route advertised to R3(13.13.13.3)
Finally, verify BGP table and routing table on all peer routers.
R2#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 14, local router ID is 2.2.2.2
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 0.0.0.0 12.12.12.1 0 100 i
*> 1.1.1.0/24 12.12.12.1 0 0 100 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 12.12.12.1 0 100 300 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 12.12.12.1 0 100 i
R2#sh ip route 0.0.0.0
Routing entry for 0.0.0.0/0, supernet
Known via "bgp 200", distance 20, metric 0, candidate default path
Tag 100, type external
Last update from 12.12.12.1 00:08:27 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 12.12.12.1, from 12.12.12.1, 00:08:27 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 1
AS Hops 1
Route tag 100
MPLS label: none
R3#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 11, local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 13.13.13.1 0 0 100 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 13.13.13.1 0 100 200 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 13.13.13.1 0 100 i
R3#sh ip route 0.0.0.0
% Network not in table
R4#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 11, local router ID is 4.4.4.4
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
r>i 1.1.1.0/24 14.14.14.1 0 100 0 i
*>i 2.2.2.0/24 14.14.14.1 0 100 0 200 i
*>i 3.3.3.0/24 14.14.14.1 0 100 0 300 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
R4#sh ip route 0.0.0.0
% Network not in table