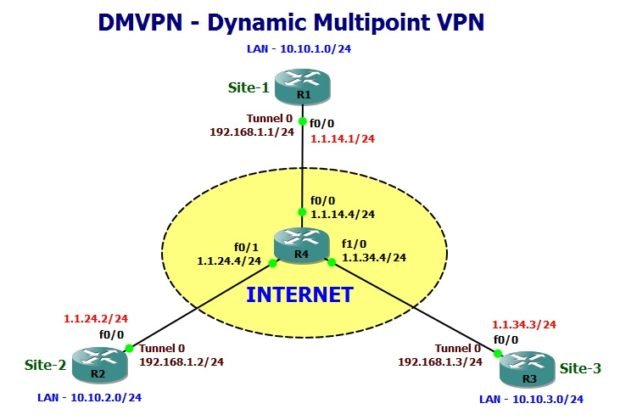
DMVPN Phase 1 – Hub to Spoke Design
DMVPN Phase 1 provides Hub and Spoke tunnel deployment. It means GRE tunnels are only built between Hub and Spokes. There is no spoke-to-spoke tunnel. Traffic from one spoke site to another spoke site always traverse via hub.
Check this link for DMVPN basics – http://www.amolak.net/dmvpn-basics/
We will discuss DMVPN Phase 1 configuration with:
- EIGRP
- OSPF
- BGP
Here is the network topology for our discussion and configuration.
Initial configuration on devices
Site-1 Router R1: hostname R1 ! ip cef ! crypto isakmp policy 10 encr aes authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key DmVpNpR3$h@r3dK3Y address 0.0.0.0 ! ! crypto ipsec transform-set TRANSFORM-SET esp-aes esp-sha-hmac mode transport ! crypto ipsec profile PROTECT-GRE set transform-set TRANSFORM-SET ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 1.1.14.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 10.10.1.1 255.255.255.0 ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.14.4 ! Site-2 Router R2: hostname R2 ! ip cef ! crypto isakmp policy 10 encr aes authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key DmVpNpR3$h@r3dK3Y address 0.0.0.0 ! crypto ipsec transform-set TRANSFORM-SET esp-aes esp-sha-hmac mode transport ! crypto ipsec profile PROTECT-GRE set transform-set TRANSFORM-SET ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 1.1.24.2 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 10.10.2.2 255.255.255.0 ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.24.4 ! Site-3 Router R3: hostname R3 ! ip cef ! crypto isakmp policy 10 encr aes authentication pre-share group 2 crypto isakmp key DmVpNpR3$h@r3dK3Y address 0.0.0.0 ! ! crypto ipsec transform-set TRANSFORM-SET esp-aes esp-sha-hmac mode transport ! crypto ipsec profile PROTECT-GRE set transform-set TRANSFORM-SET ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 1.1.34.3 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 10.10.3.3 255.255.255.0 ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.1.34.4 ! Internet Router R4: hostname R4 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 1.1.14.4 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 1.1.24.4 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 1.1.34.4 255.255.255.0 !
DMVPN NBMA Network Behavior
DMVPN creates Non Broadcast Multi Access (NBMA) networks. By default, NBMA network do not support multicast traffic and multicast traffic is required to enable dynamic routing protocols.
“ip nhrp map multicast dynamic“ command is used under hub router tunnel interface to enable support of multicast traffic. This allows each spoke to register as a receiver of multicast traffic, causing the hub to replicate and forward multicast traffic to the spoke routers.
“ip nhrp map multicast <hub nbma ip>” command is used under spoke routers tunnel interface. It ensures multicast traffic is sent only from spokes to the hub and not from spoke to spoke.
With this set up, routing adjacencies are only formed between hub and spokes. Spokes do not form routing adjacencies with each other.
ip nhrp network-id
The NHRP network ID is used to define the NHRP domain for an NHRP interface and differentiate between multiple NHRP domains or networks, when two or more NHRP domains (GRE tunnel interfaces) are available on the same NHRP router. The NHRP network ID is used to help keep two NHRP networks (clouds) separate from each other when both are configured on the same router. NHRP network IDs are locally significant and can be different.
DMVPN Phase 1 configuration with EIGRP
---------- R1 - Hub: ---------- Since all spoke routers are configured with tunnel mode GRE (p2p GRE), they can send traffic via Hub only. So spoke routers do not require specific routes of each other. Hub router would advertise a single EIGRP summary route to all spoke routers. Basically Hub router is telling spokes if you want to reach any specific subnet from this summary route, send that traffic to me, I will forward it to actual destination spoke site. interface Tunnel0 bandwidth 4096 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 no ip redirects ip mtu 1400 ip nhrp authentication NhRp@UtH ip nhrp map multicast dynamic ip nhrp network-id 100 ip summary-address eigrp 100 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 tunnel source FastEthernet0/0 tunnel mode gre multipoint tunnel protection ipsec profile PROTECT-GRE ! router eigrp 100 network 10.10.1.1 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 ------------ R2 - Spoke: ------------ interface Tunnel0 bandwidth 4096 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 ip mtu 1400 ip nhrp authentication NhRp@UtH ip nhrp map multicast 1.1.14.1 ip nhrp map 192.168.1.1 1.1.14.1 ip nhrp network-id 100 ip nhrp nhs 192.168.1.1 ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 tunnel source FastEthernet0/0 tunnel destination 1.1.14.1 tunnel protection ipsec profile PROTECT-GRE ! router eigrp 100 network 10.10.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.2 0.0.0.0 ----------- R3 - Spoke: ----------- interface Tunnel0 bandwidth 4096 ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 ip mtu 1400 ip nhrp authentication NhRp@UtH ip nhrp map multicast 1.1.14.1 ip nhrp map 192.168.1.1 1.1.14.1 ip nhrp network-id 100 ip nhrp nhs 192.168.1.1 ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 tunnel source FastEthernet0/0 tunnel destination 1.1.14.1 tunnel protection ipsec profile PROTECT-GRE ! router eigrp 100 network 10.10.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.3 0.0.0.0
Verification:
- Tunnel mode is mGRE on Hub Router. - Tunnel mode is GRE (Point-to-Point GRE) on Spoke Routers. R1: R1#sh int t0 Tunnel0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Tunnel Internet address is 192.168.1.1/24 MTU 17874 bytes, BW 4096 Kbit/sec, DLY 50000 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation TUNNEL, loopback not set Keepalive not set Tunnel source 1.1.14.1 (FastEthernet0/0) Tunnel Subblocks: src-track: Tunnel0 source tracking subblock associated with FastEthernet0/0 Set of tunnels with source FastEthernet0/0, 1 member (includes iterators), on interface <OK> Tunnel protocol/transport multi-GRE/IP Key disabled, sequencing disabled Checksumming of packets disabled Tunnel TTL 255, Fast tunneling enabled Tunnel transport MTU 1434 bytes Tunnel transmit bandwidth 8000 (kbps) Tunnel receive bandwidth 8000 (kbps) Tunnel protection via IPSec (profile "PROTECT-GRE") <snip> R2: R2#sh int t0 Tunnel0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Tunnel Internet address is 192.168.1.2/24 MTU 17874 bytes, BW 4096 Kbit/sec, DLY 50000 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation TUNNEL, loopback not set Keepalive not set Tunnel source 1.1.24.2 (FastEthernet0/0), destination 1.1.14.1 Tunnel Subblocks: src-track: Tunnel0 source tracking subblock associated with FastEthernet0/0 Set of tunnels with source FastEthernet0/0, 1 member (includes iterators), on interface <OK> Tunnel protocol/transport GRE/IP Key disabled, sequencing disabled Checksumming of packets disabled Tunnel TTL 255, Fast tunneling enabled Tunnel transport MTU 1434 bytes Tunnel transmit bandwidth 8000 (kbps) Tunnel receive bandwidth 8000 (kbps) Tunnel protection via IPSec (profile "PROTECT-GRE") <snip> R3: R3#sh int t0 Tunnel0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is Tunnel Internet address is 192.168.1.3/24 MTU 17874 bytes, BW 4096 Kbit/sec, DLY 50000 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation TUNNEL, loopback not set Keepalive not set Tunnel source 1.1.34.3 (FastEthernet0/0), destination 1.1.14.1 Tunnel Subblocks: src-track: Tunnel0 source tracking subblock associated with FastEthernet0/0 Set of tunnels with source FastEthernet0/0, 1 member (includes iterators), on interface <OK> Tunnel protocol/transport GRE/IP Key disabled, sequencing disabled Checksumming of packets disabled Tunnel TTL 255, Fast tunneling enabled Tunnel transport MTU 1434 bytes Tunnel transmit bandwidth 8000 (kbps) Tunnel receive bandwidth 8000 (kbps) Tunnel protection via IPSec (profile "PROTECT-GRE") <snip> - Routing adjacencies are Hub to Spokes only R1#show ip eigrp neighbors EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(100) H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num 1 192.168.1.3 Tu0 11 00:19:56 191 1146 0 16 0 192.168.1.2 Tu0 14 00:19:56 178 1068 0 16 R2#show ip eigrp neighbors EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(100) H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num 0 192.168.1.1 Tu0 11 00:20:37 779 4674 0 10 R3#show ip eigrp neighbors EIGRP-IPv4 Neighbors for AS(100) H Address Interface Hold Uptime SRTT RTO Q Seq (sec) (ms) Cnt Num 0 192.168.1.1 Tu0 14 00:20:39 183 1098 0 11 - Routing Table R1#show ip route eigrp | beg Gate Gateway of last resort is 1.1.14.4 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 3 masks D 10.10.0.0/16 is a summary, 00:14:48, Null0 D 10.10.2.0/24 [90/1907456] via 192.168.1.2, 00:22:02, Tunnel0 D 10.10.3.0/24 [90/1907456] via 192.168.1.3, 00:22:04, Tunnel0 R2#show ip route eigrp | beg Gate Gateway of last resort is 1.1.24.4 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 3 masks D 10.10.0.0/16 [90/1907456] via 192.168.1.1, 00:15:06, Tunnel0 R3#show ip route eigrp | beg Gate Gateway of last resort is 1.1.34.4 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 3 masks D 10.10.0.0/16 [90/1907456] via 192.168.1.1, 00:15:17, Tunnel0 - Spoke (R2) to Spoke (R3) traffic traverse via Hub R2#ping 10.10.3.3 so 10.10.2.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.3.3, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 10.10.2.2 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 192/199/212 ms R2#trace 10.10.3.3 so 10.10.2.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 10.10.3.3 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 192.168.1.1 144 msec 140 msec 136 msec << Hub R1 Tunnel IP 2 192.168.1.3 204 msec * 196 msec << Spoke R3 Tunnel IP
- DMVPN status on Hub R1#sh dmvpn Legend: Attrb --> S - Static, D - Dynamic, I - Incomplete N - NATed, L - Local, X - No Socket # Ent --> Number of NHRP entries with same NBMA peer NHS Status: E --> Expecting Replies, R --> Responding, W --> Waiting UpDn Time --> Up or Down Time for a Tunnel ====================================================================== Interface: Tunnel0, IPv4 NHRP Details Type:Hub, NHRP Peers:2, # Ent Peer NBMA Addr Peer Tunnel Add State UpDn Tm Attrb ----- --------------- --------------- ----- -------- ----- 1 1.1.24.2 192.168.1.2 UP 01:21:07 D 1 1.1.34.3 192.168.1.3 UP 01:21:11 D R1#sh ip nhrp 192.168.1.2/32 via 192.168.1.2 Tunnel0 created 01:50:50, expire 01:29:09 Type: dynamic, Flags: unique registered used NBMA address: 1.1.24.2 192.168.1.3/32 via 192.168.1.3 Tunnel0 created 01:50:54, expire 01:29:05 Type: dynamic, Flags: unique registered used NBMA address: 1.1.34.3 - DMVPN status on Spoke Routers R2#sh dmvpn Legend: Attrb --> S - Static, D - Dynamic, I - Incomplete N - NATed, L - Local, X - No Socket # Ent --> Number of NHRP entries with same NBMA peer NHS Status: E --> Expecting Replies, R --> Responding, W --> Waiting UpDn Time --> Up or Down Time for a Tunnel ===================================================================== Interface: Tunnel0, IPv4 NHRP Details Type:Spoke, NHRP Peers:1, # Ent Peer NBMA Addr Peer Tunnel Add State UpDn Tm Attrb ----- --------------- --------------- ----- -------- ----- 1 1.1.14.1 192.168.1.1 UP 01:22:47 S R2#sh ip nhrp 192.168.1.1/32 via 192.168.1.1 Tunnel0 created 01:53:57, never expire Type: static, Flags: NBMA address: 1.1.14.1 R3#sh dmvpn Legend: Attrb --> S - Static, D - Dynamic, I - Incomplete N - NATed, L - Local, X - No Socket # Ent --> Number of NHRP entries with same NBMA peer NHS Status: E --> Expecting Replies, R --> Responding, W --> Waiting UpDn Time --> Up or Down Time for a Tunnel ==================================================================== Interface: Tunnel0, IPv4 NHRP Details Type:Spoke, NHRP Peers:1, # Ent Peer NBMA Addr Peer Tunnel Add State UpDn Tm Attrb ----- --------------- --------------- ----- -------- ----- 1 1.1.14.1 192.168.1.1 UP 01:23:09 S R3#sh ip nhrp 192.168.1.1/32 via 192.168.1.1 Tunnel0 created 01:54:39, never expire Type: static, Flags: NBMA address: 1.1.14.1
DMVPN Phase 1 configuration with OSPF
- Hub router tunnel would be OSPF network type point-to-multipoint - Spoke routers tunnel would be OSPF network type point-to-point - OSPF hello timers must match on tunnel interface on Hub and Spokes - Route summarization is not feasible in single OSPF area R1: interface Tunnel0 bandwidth 4096 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 no ip redirects ip mtu 1400 ip nhrp authentication NhRp@UtH ip nhrp map multicast dynamic ip nhrp network-id 100 ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 ip ospf network point-to-multipoint ip ospf hello-interval 10 tunnel source FastEthernet0/0 tunnel mode gre multipoint tunnel protection ipsec profile PROTECT-GRE ! router ospf 1 network 10.10.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 R2: interface Tunnel0 bandwidth 4096 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 ip mtu 1400 ip nhrp authentication NhRp@UtH ip nhrp map multicast 1.1.14.1 ip nhrp map 192.168.1.1 1.1.14.1 ip nhrp network-id 100 ip nhrp nhs 192.168.1.1 ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 tunnel source FastEthernet0/0 tunnel destination 1.1.14.1 tunnel protection ipsec profile PROTECT-GRE ! router ospf 1 network 10.10.2.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 192.168.1.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 R3: interface Tunnel0 bandwidth 4096 ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 ip mtu 1400 ip nhrp authentication NhRp@UtH ip nhrp map multicast 1.1.14.1 ip nhrp map 192.168.1.1 1.1.14.1 ip nhrp network-id 100 ip nhrp nhs 192.168.1.1 ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 tunnel source FastEthernet0/0 tunnel destination 1.1.14.1 tunnel protection ipsec profile PROTECT-GRE ! router ospf 1 network 10.10.3.3 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 192.168.1.3 0.0.0.0 area 0
Verification
R1: R1#show ip ospf int t0 Tunnel0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 192.168.1.1/24, Area 0, Attached via Network Statement Process ID 1, Router ID 192.168.1.1, Network Type POINT_TO_MULTIPOINT, Cost: 24 Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name 0 24 no no Base Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_MULTIPOINT Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 40 Hello due in 00:00:05 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Cisco NSF helper support enabled IETF NSF helper support enabled Index 2/2, flood queue length 0 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1 Last flood scan time is 4 msec, maximum is 4 msec Neighbor Count is 2, Adjacent neighbor count is 2 Adjacent with neighbor 192.168.1.3 Adjacent with neighbor 192.168.1.2 Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s) R1#show ip ospf ne Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 192.168.1.3 0 FULL/ - 00:00:33 192.168.1.3 Tunnel0 192.168.1.2 0 FULL/ - 00:00:34 192.168.1.2 Tunnel0 R1#show ip route ospf | beg Gate Gateway of last resort is 1.1.14.4 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks O 10.10.2.0/24 [110/25] via 192.168.1.2, 00:04:05, Tunnel0 O 10.10.3.0/24 [110/25] via 192.168.1.3, 00:03:45, Tunnel0 R2: R2#show ip ospf int t0 Tunnel0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 192.168.1.2/24, Area 0, Attached via Network Statement Process ID 1, Router ID 192.168.1.2, Network Type POINT_TO_POINT, Cost: 24 Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name 0 24 no no Base Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 40 Hello due in 00:00:08 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Cisco NSF helper support enabled IETF NSF helper support enabled Index 2/2, flood queue length 0 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1 Last flood scan time is 4 msec, maximum is 4 msec Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1 Adjacent with neighbor 192.168.1.1 Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s) R2#show ip ospf ne Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 192.168.1.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:31 192.168.1.1 Tunnel0 R2#show ip route ospf | beg Gate Gateway of last resort is 1.1.24.4 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks O 10.10.1.0/24 [110/25] via 192.168.1.1, 00:05:12, Tunnel0 O 10.10.3.0/24 [110/49] via 192.168.1.1, 00:04:35, Tunnel0 192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks O 192.168.1.1/32 [110/24] via 192.168.1.1, 00:05:12, Tunnel0 R3: R3#show ip ospf int t0 Tunnel0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 192.168.1.3/24, Area 0, Attached via Network Statement Process ID 1, Router ID 192.168.1.3, Network Type POINT_TO_POINT, Cost: 24 Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name 0 24 no no Base Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State POINT_TO_POINT Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 40 Hello due in 00:00:02 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Cisco NSF helper support enabled IETF NSF helper support enabled Index 2/2, flood queue length 0 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1 Last flood scan time is 4 msec, maximum is 4 msec Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1 Adjacent with neighbor 192.168.1.1 Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s) R3#show ip ospf ne Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 192.168.1.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:31 192.168.1.1 Tunnel0 R3#show ip route ospf | beg Gate Gateway of last resort is 1.1.34.4 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks O 10.10.1.0/24 [110/25] via 192.168.1.1, 00:05:40, Tunnel0 O 10.10.2.0/24 [110/49] via 192.168.1.1, 00:05:40, Tunnel0 192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks O 192.168.1.1/32 [110/24] via 192.168.1.1, 00:05:40, Tunnel0 Spoke to Spoke traffic: R2#ping 10.10.3.3 so 10.10.2.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.3.3, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 10.10.2.2 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 196/201/208 ms R2#trace 10.10.3.3 so 10.10.2.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 10.10.3.3 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 192.168.1.1 152 msec 120 msec 164 msec << Hub Tunnel IP 2 192.168.1.3 236 msec * 220 msec << Spoke-3 Tunnel IP
DMVPN Phase 1 configuration with BGP
- "bgp listen range ....." command can be used to define a range of IP address of BGP neighbors on hub router - "bgp listen limit xx" command can be used to set the limit of dynamic BGP neighbors - Hub router would act as BGP Route-reflector server - Spoke routers would be BGP route-reflector clients - As spokes would communicate via hub only, it is inefficient to advertise all specific prefixes to spoke BGP peers - Hub Router would advertise summary route to spokes R1: interface Tunnel0 bandwidth 4096 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 no ip redirects ip mtu 1400 ip nhrp authentication NhRp@UtH ip nhrp network-id 100 ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 tunnel source FastEthernet0/0 tunnel mode gre multipoint tunnel protection ipsec profile PROTECT-GRE ! router bgp 65001 bgp router-id 192.168.1.1 bgp log-neighbor-changes bgp listen range 192.168.1.0/24 peer-group DMVPN-SPOKES bgp listen limit 50 network 10.10.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 aggregate-address 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 summary-only neighbor DMVPN-SPOKES peer-group neighbor DMVPN-SPOKES remote-as 65001 neighbor DMVPN-SPOKES route-reflector-client R2: interface Tunnel0 bandwidth 4096 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 ip mtu 1400 ip nhrp authentication NhRp@UtH ip nhrp map 192.168.1.1 1.1.14.1 ip nhrp network-id 100 ip nhrp nhs 192.168.1.1 ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 tunnel source FastEthernet0/0 tunnel destination 1.1.14.1 tunnel protection ipsec profile PROTECT-GRE ! router bgp 65001 bgp router-id 192.168.1.2 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 10.10.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 neighbor 192.168.1.1 remote-as 65001 R3: interface Tunnel0 bandwidth 4096 ip address 192.168.1.3 255.255.255.0 ip mtu 1400 ip nhrp authentication NhRp@UtH ip nhrp map 192.168.1.1 1.1.14.1 ip nhrp network-id 100 ip nhrp nhs 192.168.1.1 ip tcp adjust-mss 1360 tunnel source FastEthernet0/0 tunnel destination 1.1.14.1 tunnel protection ipsec profile PROTECT-GRE ! router bgp 65001 bgp router-id 192.168.1.3 bgp log-neighbor-changes network 10.10.3.0 mask 255.255.255.0 neighbor 192.168.1.1 remote-as 65001
Verification
R1: R1#show ip bgp summary BGP router identifier 192.168.1.1, local AS number 65001 BGP table version is 8, main routing table version 8 4 network entries using 592 bytes of memory 4 path entries using 256 bytes of memory 3/3 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 408 bytes of memory 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory BGP using 1256 total bytes of memory BGP activity 4/0 prefixes, 4/0 paths, scan interval 60 secs Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd *192.168.1.2 4 65001 38 40 8 0 0 00:30:25 1 *192.168.1.3 4 65001 37 39 8 0 0 00:30:09 1 * Dynamically created based on a listen range command Dynamically created neighbors: 2, Subnet ranges: 1 BGP peergroup DMVPN-SPOKES listen range group members: 192.168.1.0/24 Total dynamically created neighbors: 2/(50 max), Subnet ranges: 1 R1#show ip bgp BGP table version is 8, local router ID is 192.168.1.1 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *> 10.10.0.0/16 0.0.0.0 32768 i s> 10.10.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i s>i 10.10.2.0/24 192.168.1.2 0 100 0 i s>i 10.10.3.0/24 192.168.1.3 0 100 0 i R1#show ip route bgp | beg Gate Gateway of last resort is 1.1.14.4 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 3 masks B 10.10.0.0/16 [200/0] via 0.0.0.0, 00:30:49, Null0 B 10.10.2.0/24 [200/0] via 192.168.1.2, 00:30:49 B 10.10.3.0/24 [200/0] via 192.168.1.3, 00:29:46 R2: R2#show ip bgp sum BGP router identifier 192.168.1.2, local AS number 65001 BGP table version is 5, main routing table version 5 2 network entries using 296 bytes of memory 2 path entries using 128 bytes of memory 2/2 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 272 bytes of memory 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory BGP using 696 total bytes of memory BGP activity 3/1 prefixes, 3/1 paths, scan interval 60 secs Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 192.168.1.1 4 65001 41 40 5 0 0 00:31:43 1 R2#show ip bgp BGP table version is 5, local router ID is 192.168.1.2 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i 10.10.0.0/16 192.168.1.1 0 100 0 i *> 10.10.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i R2#show ip route bgp | beg Gate Gateway of last resort is 1.1.24.4 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 3 masks B 10.10.0.0/16 [200/0] via 192.168.1.1, 00:31:53 R3: R3#show ip bgp sum BGP router identifier 192.168.1.3, local AS number 65001 BGP table version is 3, main routing table version 3 2 network entries using 296 bytes of memory 2 path entries using 128 bytes of memory 2/2 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 272 bytes of memory 0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory 0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory BGP using 696 total bytes of memory BGP activity 2/0 prefixes, 2/0 paths, scan interval 60 secs Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd 192.168.1.1 4 65001 41 39 3 0 0 00:32:08 1 R3#show ip bgp BGP table version is 3, local router ID is 192.168.1.3 Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal, r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter, x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed, Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path *>i 10.10.0.0/16 192.168.1.1 0 100 0 i *> 10.10.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i R3#show ip route bgp | beg Gate Gateway of last resort is 1.1.34.4 to network 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 3 masks B 10.10.0.0/16 [200/0] via 192.168.1.1, 00:31:29 Spoke-to-Spoke traffic: R2#ping 10.10.3.3 so 10.10.2.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.3.3, timeout is 2 seconds: Packet sent with a source address of 10.10.2.2 !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 180/192/204 ms R2#trace 10.10.3.3 so 10.10.2.2 Type escape sequence to abort. Tracing the route to 10.10.3.3 VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id) 1 192.168.1.1 140 msec 176 msec 140 msec << Hub Tunnel IP 2 192.168.1.3 224 msec * 220 msec << Spoke-3 Tunnel IP
As we have seen that spoke-to-spoke traffic always traverse via hub in phase 1 design. In a large network, It increases overhead on hub router. Also spokes has to use sub-optimal routing path for traffic between spoke sites. The shortcomings of DMVPN phase 1 are addressed in Phase 2 design, which we will discuss in next blog.